United Parcel Service: fundamental analysis and UPS share price forecast for 2026
UPS shares appear resilient following the Q3 2025 results, supported by improving profitability and a moderately positive outlook. This article provides a fundamental and technical analysis of UPS shares, along with a forecast for 2026.
United Parcel Service (NYSE: UPS) reported revenue of 21.4 billion USD. Non-GAAP operating income amounted to 2.1 billion USD, with an operating margin of 10.0%, while non-GAAP earnings per share reached 1.74 USD. The results exceeded market expectations: analysts had forecast revenue of around 20.8 billion USD and earnings per share of approximately 1.30 USD, indicating a strong report. At the same time, revenue declined year-on-year, but profitability improved due to the company’s cost-reduction program. Results were further supported by a one-off sale-leaseback transaction involving five facilities, which generated 330 million USD in pre-tax profit and added around 0.30 USD to earnings per share.
Performance by segment was mixed. In the US, revenue declined to 14.22 billion USD, while operating profit amounted to 905 million USD. The international business, by contrast, delivered growth, with revenue reaching 4.67 billion USD and an operating profit of 691 million USD. The Supply Chain Solutions segment generated revenue of 2.52 billion USD, which was below prior levels.
The outlook for Q4 2025 is moderately positive. The company expects revenue of around 24.0 billion USD and a non-GAAP operating margin of 11.0–11.5%. For the full 2025 financial year, UPS reaffirmed its plans for capital expenditure of approximately 3.5 billion USD, dividend payments of around 5.5 billion USD, and pension contributions of 1.4 billion USD.
This article examines United Parcel Service, Inc., outlines the sources of its revenue, summarises UPS’s performance for Q1, Q2, and Q3 of the 2025 financial year, and presents expectations for the upcoming quarter. It also includes a technical analysis of UPS shares, on the basis of which a forecast for UPS shares for the 2026 calendar year is developed.
About United Parcel Service, Inc.
United Parcel Service (UPS) is the world’s largest logistics and courier company, specialising in freight and parcel delivery as well as logistics solutions. Founded in Seattle, US, by James E. Casey and Claude Ryan in 1907 as the American Messenger Company, it was renamed United Parcel Service in 1919 as operations expanded beyond Seattle. Its initial public offering took place on 10 November 1999 on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker UPS. The company provides express parcel delivery across the US and globally, along with international logistics, contract logistics, supply chain management, and specialised solutions for a range of industries, including e-commerce, healthcare, and manufacturing. It is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. UPS’ primary competitors include FedEx (NYSE: FDX) and DHL (XETR: DHL), part of the Deutsche Post Group, along with regional and local delivery operators, including national postal services and new market entrants such as Amazon Logistics.
Image of the company name United Parcel Service, Inc.United Parcel Service, Inc.’s business model
UPS’s business model is built around a wide range of logistics and transportation services. The company’s revenue is derived from the following key segments:
- US Domestic Package (domestic delivery across the US): this is UPS’s primary revenue stream, comprising parcel delivery to individuals (B2C) and corporate clients (B2B) across the US. Revenue is generated through express delivery services, including UPS Next Day Air, as well as standard and economy options, with additional charges applied for overweight parcels, urgent shipments, and residential delivery.
- International Package (international shipments): this includes revenue from international parcel and freight deliveries worldwide, covering both export and import operations. UPS operates in over 220 countries, and the international division generates particularly high margins from the express delivery of documents and commercial shipments.
- Supply Chain Solutions (logistics and supply chain operations): this segment includes revenue from comprehensive logistics solutions, including contract logistics (warehousing, packaging, and inventory management), specialised solutions for healthcare, manufacturing, e-commerce and technology, LTL transportation services, ocean and air freight, as well as supply chain management and reverse logistics services.
- Surcharges and Value-Added Services: this category includes fuel surcharges, peak load charges, insurance, tracking, rerouting, and other related services, which increase the average revenue per shipment.
Thus, UPS generates revenue through a diversified portfolio of logistics services, serving both the mass segment (retail clients) and the large corporate sector with tailored supply chain solutions.
United Parcel Service, Inc. Q1 2025 results
On 23 April 2025, UPS published its results for Q1 of the 2025 financial year, which ended on 31 March 2025. Below is its key financial data compared to the corresponding period of last year:
- Revenue: 21.55 billion USD (–1%)
- Net income: 1.27 billion USD (+4%)
- Earnings per share: 1.49 USD (+4%)
- Operating margin: 8.20% (+20 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- US Domestic Segment: 14.46 billion USD (+1%)
- Operating profit: 1.01 billion USD (+19%)
- International Segment: 4.37 billion USD (+3%)
- Operating profit: 654 million USD (–4%)
- Supply Chain Solutions: 2.71 billion USD (–15%)
- Operating profit: 98 million USD (–55%)
UPS’ Q1 fiscal 2025 report demonstrated the company’s agile adaptation to external challenges and its focused efforts to enhance operational efficiency and maintain profitability. With revenue down 1% to 21.5 billion USD, non-GAAP adjusted EPS was 1.49 USD, exceeding the consensus forecast by over 8%, confirming the stability of key business areas.
CEO Carol Tomé noted that UPS is undertaking the largest transformation of its logistics network in the company’s history, with plans to save 3.5 billion USD this year by closing 73 facilities and laying off 20,000 employees. This move enables the company to offset lower volumes, including a decline in orders from Amazon and tariff pressure on international shipments. UPS is adapting its structure to meet current demand, becoming more compact and efficient.
Although management did not update its full-year 2025 outlook due to macroeconomic uncertainty, particularly relating to tariffs, it provided guidance for Q2. Revenue is expected to reach 21 billion USD, with US parcel delivery volumes projected to decline by 9%. International margins are anticipated to remain in the mid-double-digit range (percentage terms). Margins in the US delivery segment are also forecast to rise by 30 basis points, supported by the impact of restructuring.
UPS is prioritising strict cost optimisation over revenue growth, and its Q2 guidance reflects a realistic, cautious stance amid ongoing uncertainty. If the company succeeds in implementing the planned 3.5 billion USD in savings, including potential further restructuring, it could emerge from the current cycle significantly more profitable and resilient.
United Parcel Service, Inc. Q2 2025 financial results
On 29 July 2025, UPS released its results for Q2 of the 2025 financial year, which ended on 30 June 2025. The key financial metrics compared with the same period last year are as follows:
- Revenue: 21.22 billion USD (–3%)
- Net profit: 1.31 billion USD (–14%)
- Earnings per share: 1.55 USD (–13%)
- Operating margin: 8.80% (–60 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- US Domestic Segment: 14.08 billion USD (–1%)
- Operating profit: 0.98 billion USD (–1%)
- International Segment: 4.49 billion USD (+3%)
- Operating profit: 682 million USD (–17%)
- Supply Chain Solutions: 2.65 billion USD (–18%)
- Operating profit: 212 million USD (–13%)
UPS reported Q2 FY2025 revenue of 21.2 billion USD and non-GAAP EPS of 1.55 USD. Sales exceeded analyst forecasts, but earnings came in slightly below consensus.
In the US, results were weaker: revenue declined, parcel volumes fell by 7%, and per-parcel delivery costs increased, weighing on margins. The international business presented the opposite picture: volume growth of nearly 4% and a profitability level of around 15% made this segment the strongest performer. The Supply Chain Solutions division was impacted by the sale of Coyote a year earlier, resulting in lower revenue. Free cash flow for the first half of the year was 742 million USD – sufficient to cover dividends and investment, while the company continues to build resilience through cost savings.
The main weak spots for UPS are declining volumes in the US, rising per-parcel costs, and the lingering impact of the Coyote divestment. Additional pressure comes from new tariffs on low-value parcels from China, which are weighing on budget marketplaces and last-mile delivery.
On the positive side, UPS maintains high margins in its international segment and is firmly implementing its optimisation program, which is expected to deliver around 3.5 billion USD in cost savings in 2025. The company is also reducing reliance on Amazon, accepting lower volumes in exchange for improved profitability.
While UPS does not provide quarterly guidance, it reaffirmed its full-year 2025 plan, which includes capital expenditures of around 3.5 billion USD, dividends of approximately 5.5 billion USD, and pension contributions of about 1.4 billion USD.
United Parcel Service, Inc. Q3 2025 financial results
On 28 October 2025, UPS released its results for Q3 of the 2025 financial year, which ended on 30 September 2025. Key financial figures compared with the same period last year are as follows:
- Revenue: 21.42 billion USD (–4%)
- Net profit (non-GAAP): 1.48 billion USD (–2%)
- Earnings per share (non-GAAP): 1.74 USD (–1%)
- Operating margin: 10.00% (+110 basis points)
Revenue by segment:
- US Domestic segment: 14.22 billion USD (–3%)
- Operating profit: 0.91 billion USD (–2%)
- International segment: 4.67 billion USD (+6%)
- Operating profit: 691 million USD (–13%)
- Supply Chain Solutions: 2.52 billion USD (–22%)
- Operating profit: 536 million USD (+97%)
In Q3 of the 2025 financial year, United Parcel Service reported non-GAAP results that were materially better than market expectations. Revenue totalled 21.4 billion USD, operating income reached 2.1 billion USD, operating margin stood at 10%, and earnings per share came in at 1.74 USD. Analysts had expected revenue of around 20.8 billion USD and earnings per share of approximately 1.30 USD, meaning the report exceeded expectations on both revenue and profitability.
On a year-on-year basis, revenue declined by 4%, but the company improved margins thanks to a more favourable revenue mix and cost reductions. As part of its cost-saving program, UPS reduced headcount and closed several facilities, thereby supporting overall profitability. In the US, revenue declined due to lower volumes, but this was partially offset by a 10% increase in revenue per package. The international business performed more strongly, with revenue growth of 6% and margins remaining at a healthy level.
During the quarter, UPS generated approximately 330 million USD in pre-tax profit from a sale-and-leaseback transaction involving real estate assets, adding around 0.30 USD to earnings per share. This was a one-off factor; however, even after excluding it, earnings would still have exceeded market expectations.
Management provided a moderately positive outlook for the next quarter. For Q4 2025, the company expects revenue of around 24.0 billion USD and an operating margin of 11.0–11.5%.
For the full 2025 financial year, UPS largely reaffirmed its capital allocation plans: capital expenditure of 3.5 billion USD, dividends of 5.5 billion USD, pension contributions of 1.4 billion USD, and a share buyback program of 1.0 billion USD, which has already been completed.
Fundamental analysis for United Parcel Service, Inc.
Below is a fundamental analysis for UPS based on the results of Q3 2025:
- Liquidity and balance sheet: as of the end of Q3 2025, UPS held 6.764 billion USD in cash. Current assets totalled 18.99 billion USD, while current liabilities stood at 14.55 billion USD, resulting in a current ratio of approximately 1.30. Shareholders’ equity totalled 15.85 billion USD, down from the end of 2024, reflecting the company’s substantial capital returns to shareholders. Importantly, part of UPS’s liquidity is held overseas: the company notes that around 3.3 billion USD in cash, equivalents, and marketable securities were held by foreign subsidiaries, and this proportion may fluctuate during the year.
- Cash flows: over the first nine months of 2025, operating cash flow totalled 5.15 billion USD, down from 6.81 billion USD in the same period last year, indicating a year-on-year decline in cash generation. Capital expenditure over the nine months totalled 2.97 billion USD, resulting in free cash flow (operating cash flow minus CapEx) of 2.18 billion USD.
- Dividends and coverage: over the first nine months, UPS paid 4.04 billion USD in dividends, exceeding free cash flow for the same period. This indicates that, during the first nine months of the year, dividends and share buybacks were supported not only by operating cash flow but also by other sources, such as debt issuance and the monetisation of certain real estate assets through sale-leaseback transactions. For the full 2025 financial year, the company reaffirmed its expectation of dividend payments of approximately 5.5 billion USD, subject to approval by the Board of Directors.
- Debt: as of the end of Q3 2025, United Parcel Service’s total debt, including finance leases, amounted to 25.03 billion USD, of which 23.85 billion USD was long-term debt. Near-term maturities and the current portion of debt and leases are relatively modest, at 932 million USD. UPS also has an undrawn revolving credit facility of 2.0 billion USD, maturing in November 2029, providing an additional liquidity buffer if required. In addition to debt, other fixed obligations must be considered. Operating lease liabilities amount to 0.74 billion USD in the short term and 3.69 billion USD in the long term. The company also carries pension and post-retirement obligations totalling 6.19 billion USD, which increases the long-term burden on the company’s cash flows.
Fundamental analysis for UPS – conclusion.
United Parcel Service appears solvent on its balance sheet. The company holds 6.76 billion USD in cash, maintains a current ratio of approximately 1.30, and retains access to bank credit facilities.
The primary risk lies not in debt levels, but in cash flow dynamics. Over the first nine months, operating cash flow declined to 5.15 billion USD, while dividend payments of 4.04 billion USD and share buybacks of 1.0 billion USD together exceeded free cash flow for the period. As a result, part of shareholder returns was effectively financed through debt and one-off sources, including sale-leaseback transactions.
At present, this does not appear critical, but it does make financial sustainability increasingly dependent on UPS’s ability to maintain current profitability and restore cash flow in the coming quarters.
Expert forecasts for United Parcel Service, Inc. stock
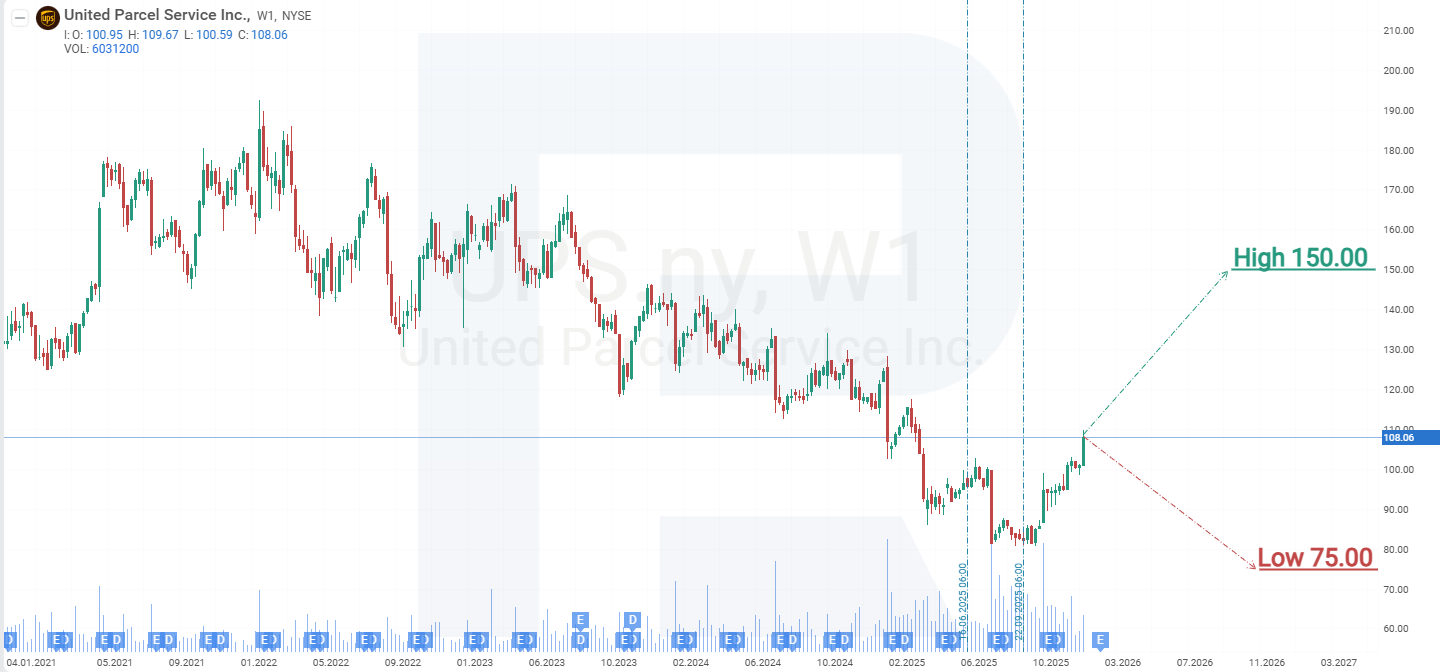
- Barchart: 11 of 29 analysts rated UPS shares as Strong Buy, 1 as Moderate Buy, 15 as Hold, 1 as Sell, and 1 as Strong Sell. The upper price target is 126 USD, and the lower bound is 75 USD.
- MarketBeat: 10 of 31 analysts assigned a Buy rating to the shares, 18 issued Hold recommendations, and 3 rated them Sell. The upper price target is 150 USD, and the lower bound is 75 USD.
- TipRanks: 9 of 19 surveyed analysts rated the shares as Buy, 9 as Hold, and 1 as Sell. The upper price target is 126 USD, and the lower bound is 80 USD.
- Stock Analysis: 6 of 20 experts rated the shares as Strong Buy, 2 as Buy, 9 as Hold, and 3 as Sell. The upper price target is 147 USD, and the lower bound is 75 USD.
United Parcel Service, Inc. stock price forecast for 2026
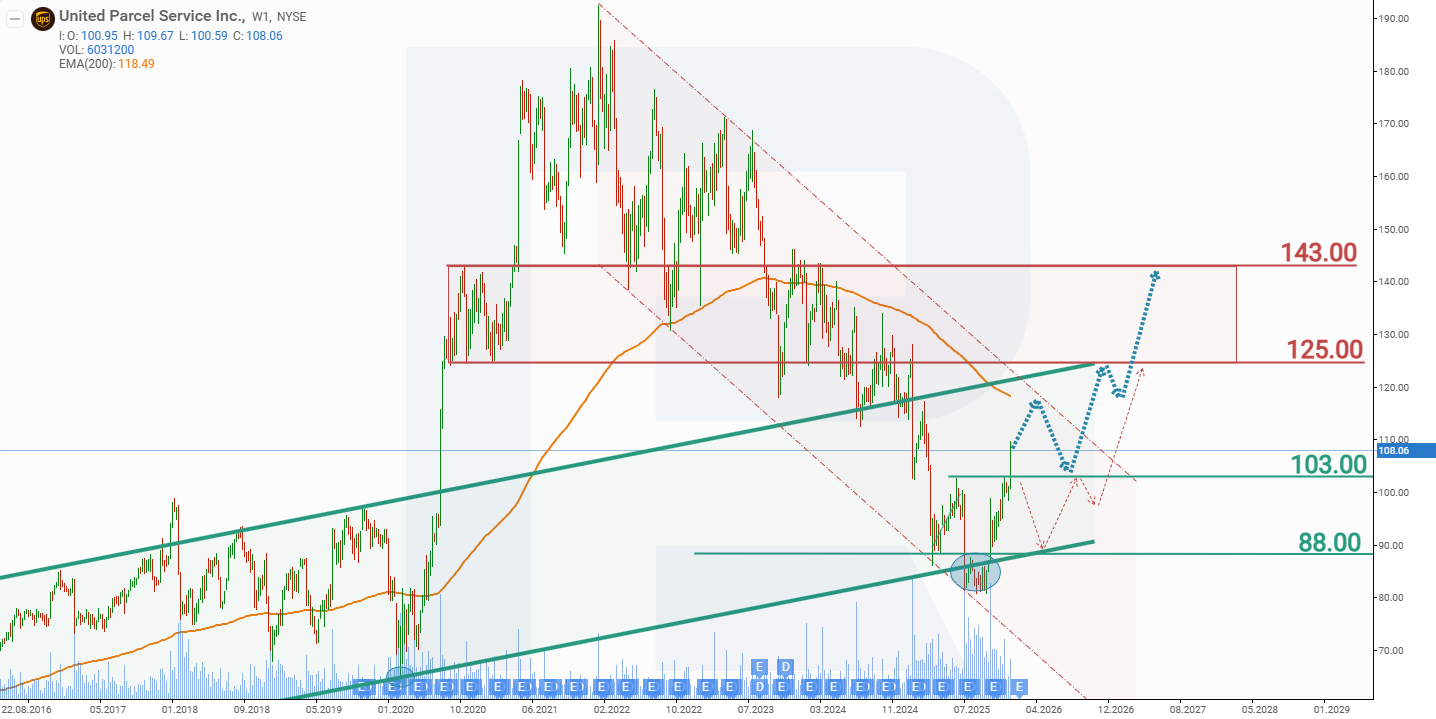
In July 2025, United Parcel Service shares reached a low of 80 USD, down 58% from the peak of 192 USD recorded in January 2022. Following a brief consolidation phase, UPS shares broke above the 88 USD resistance in October 2025 and moved higher, gaining approximately 33%. Some short-term investors who accumulated shares during the consolidation phase will likely begin to lock in profits, which could lead to a price pullback. Based on the current performance of UPS shares, the potential price scenarios for UPS in 2026 are outlined below.
The base-case forecast for UPS shares implies a test of the descending trendline at around 117 USD, followed by a rejection from this level and a decline towards support at 103 USD. Such a move would likely be driven by profit-taking among short-term investors. Thereafter, a rebound from the 103 USD support level is expected, with a resumption of the upward move towards 143 USD.
The alternative forecast for UPS stock suggests a break below support at 103 USD. In this scenario, UPS shares could decline towards 88 USD, from where a renewed advance is expected, with an upside target at 125 USD.
United Parcel Service, Inc. stock analysis and forecast for 2026Risks of investing in United Parcel Service, Inc.
stock
Investing in UPS stock entails several risks that may negatively impact its revenue and financial performance. The primary ones include:
- Economic cyclicality: demand for UPS logistics services is directly tied to overall economic activity. During recessions or periods of lower consumer demand, delivery and freight volumes decline, especially in the B2B and international trade segments.
- Rising costs (particularly labour and fuel): UPS is heavily reliant on labour and fuel. Rising diesel and aviation fuel prices, along with growing wages (driven, among other factors, by trade union contracts such as those with the Teamsters), may significantly reduce operating margins.
- Competition: the delivery market is becoming increasingly competitive. The major competitors – FedEx, DHL, Amazon Logistics, and national postal services – pursue aggressive pricing policies, invest in technology, and expand their infrastructure. Amazon, in particular, is actively developing its logistics, reducing its reliance on UPS as a contractor.
- Technology and operational disruptions: delivery delays, IT system outages, cyberattacks, accidents, or inefficient logistics chain management may lead to losses, reputational risks, and customer attrition.
- Seasonality and dependence on peak periods: a significant portion of annual revenue is generated during holiday periods, such as Q4. Any disruptions during this period, such as adverse weather conditions, personnel shortages, or logistics delays, may have a disproportionate impact.
- Investment and capital expenditure: to remain competitive, UPS requires extensive modernisation of its fleet, IT infrastructure, and warehousing logistics. Mistakes in investment decisions or excessive capital intensity can reduce returns on invested capital.
Thus, despite its status as the industry leader, UPS is subject to various factors that may limit the company’s growth or reduce its financial resilience.
Forecasts presented in this section only reflect the author’s private opinion and should not be considered as guidance for trading. RoboForex bears no responsibility for trading results based on trading recommendations described in these analytical reviews.