Tesla strengthens cash flow – analysis of the report and TSLA stock forecast
Tesla closed the quarter with record revenue and deliveries, exceeding consensus revenue estimates while slightly missing on profit. The company’s shares are approaching their all-time high.
Tesla, Inc. (NASDAQ: TSLA) reported record revenue of 28.1 billion USD (+12% y/y) in Q3 2025, with non-GAAP earnings per share of 0.50 USD. Sales exceeded analyst expectations (around 26.4 billion USD), though profit came in slightly below forecasts (around 0.55 USD).
Operating margin declined to 5.8%, reflecting higher operating expenses, increased vehicle production costs, lower income from regulatory credits, and the absence of a one-off FSD-related gain recorded a year earlier.
In Q3 2025, Tesla delivered a record 497,000 vehicles and deployed 12.5 GWh of energy storage systems, also a record.
Cash flow improved notably: operating cash flow reached 6.2 billion USD, and free cash flow approached 4 billion USD. Cash and short-term investments rose to 41.6 billion USD, ensuring a strong liquidity position.
Management did not issue quantitative guidance, citing uncertainty regarding trade, tariffs, and tax policy. Tesla expects that software, services, and AI-related projects will increasingly contribute to profitability.
The market initially reacted negatively to the decline in profitability and higher costs, putting pressure on the share price at the market open. However, investor focus soon shifted to Tesla’s strong cash metrics – robust operating and free cash flow – and its solid balance sheet. Additional positives included record results in the energy division and disciplined capital expenditure control. As a result, the company’s strong cash generation and growth potential in software, services, and AI helped ease investor concerns and restore interest in TSLA shares.
This article reviews Tesla’s operations, revenue sources, and promising business areas that could significantly enhance future income, and outlines key investment risks. It summarises the key performance indicators from the company’s Q3 and Q4 2024 and Q1–Q3 2025 reports, enabling comparison across periods, and provides a technical analysis of TSLA shares, forming the basis for the Tesla stock forecast for 2025.
About Tesla, Inc.
Tesla was founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. In 2004, Elon Musk joined the co-founders and became the largest investor, assuming the role of Chairman of the Board. In 2008, Musk became the CEO of the company.
Initially, Tesla focused exclusively on electric vehicle production, but new business areas eventually emerged. The first electric car, the Tesla Roadster, was introduced in 2008, marking the beginning of the electric vehicle manufacturing era. In 2014, the company introduced a driver assistance system, which later evolved into a fully autonomous driving system, known as Full Self-Driving.
In 2016, Tesla acquired SolarCity, a company specialising in solar panel installation, leading to the creation of Tesla Energy – a division focused on manufacturing solar panels and energy storage devices. In the near future, the company plans to launch a robotaxi service using autonomous vehicles for passenger transport, enter the freight market with the electric Tesla Semi truck, complete the development of the Optimus humanoid robot, and build the world’s most extensive Artificial Intelligence (AI) cluster for the Dojo supercomputer.
Image of Tesla, Inc.’s company nameTesla, Inc.’s main revenue streams
Tesla, Inc. generates revenue from various sources, reflecting the diversity of its products and services. The main revenue streams include:
- Vehicle sales : covers both direct sales to consumers and leasing.
- Regulatory credits : regulatory credits sold to other automakers that need them to comply with environmental regulations.
- Energy generation and storage : manufacturing and selling solar energy systems and energy storage devices – Powerwall (for residential use), Powerpack (for commercial applications), and Megapack (for large-scale energy needs).
- Services and other revenues : maintenance and repair centres, the Supercharger network, and insurance services for Tesla vehicle owners.
- Software and autonomous driving : fees for advanced driver assistance systems (Autopilot), the Full Self-Driving (FSD) package, and software updates.
- Battery and powertrain sales : supplying other companies with electric batteries, power units, and drivetrains.
- Renewable energy projects : contracts with utility companies and large energy consumers for the deployment of Tesla’s energy storage solutions.
Tesla, Inc. Q3 2024 financial results
Tesla released its Q3 2024 earnings report on 23 October, highlighting the following key figures:
- Total revenue : 25.18 billion USD (+8%)
- Net profit : 2.17 billion USD (+17%)
- Earnings per share (EPS) : 0.62 USD (+17%)
- Operating margin : 10.8% (+323 basis points)
- Capital expenditures : 3.51 billion USD (+43%)
Revenue breakdown by segment:
- Vehicle sales : 20.02 billion USD (+2%)
- Energy generation and storage : 2.38 billion USD (+52%)
- Services and other revenue : 2.79 billion USD (+29%)
In its commentary on the report, Tesla’s management noted that, despite revenue falling short of Wall Street’s consensus estimate (25.18 billion USD vs. 25.47 billion USD), the company beat profit forecasts, reporting EPS of 0.72 USD compared with the expected 0.60 USD. This was achieved through higher gross margins, supported by reduced per-unit production costs. Tesla delivered a record 462,890 electric vehicles in Q3 2024, its highest quarterly total to date.
Tesla plans to introduce more affordable vehicle models in H1 2025, expecting sales growth of 20-30% for the year. Mass production of the Cybercab is scheduled for 2026, with a target output of at least two million units. Additionally, Tesla announced that its 4680-battery cell technology is approaching cost competitiveness, which could significantly shift the economics of battery production.
Management expressed confidence in the company’s strategic initiatives and its leading position in both the automotive and energy sectors.
Tesla, Inc. Q4 2024 financial results
On 29 January, Tesla released its Q4 2024 earnings report, showing a 71% decline in net profit. The key figures from the report are as follows:
- Total revenue : 25.70 billion USD (+2%)
- Net profit : 2.12 billion USD (–71%)
- Earnings per share (EPS) : 0.60 USD (–71%)
- Operating margin : 6.2% (–204 basis points)
- Capital expenditures : 2.78 billion USD (+21%)
Revenue breakdown by segment:
- Vehicle sales : 19.80 billion USD (–8%)
- Energy generation and storage : 3.06 billion USD (+113%)
- Services and other revenue : 2.84 billion USD (+31%)
Tesla set a new record for electric vehicle deliveries in Q4 2024, with 495,570 units sold. The Tesla Model Y was the best-selling car worldwide in 2024. Elon Musk highlighted the successful production ramp-up at the Berlin and Texas Gigafactories, which played a key role in achieving these figures.
Tesla’s energy storage business also showed significant growth, driven by increased demand for products like Megapack and Powerwall. Musk emphasised that this segment is essential to Tesla’s automotive business.
The Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology continues to evolve, with the Beta program now available to more users, helping collect valuable data. Musk expressed confidence that Tesla will achieve full vehicle autonomy soon. Looking ahead, the company aims to increase vehicle deliveries by approximately 50% year-on-year while expanding its model lineup and boosting production capacity at existing factories. Tesla also focuses on cost reduction and improving operational efficiency.
A notable remark from Elon Musk concerned the Optimus robots. He stated that by the end of 2025, several thousand Optimus units will be capable of performing practical tasks, initially tested and deployed at Tesla’s factories. Musk outlined Tesla’s ambition to rapidly scale Optimus production, projecting that even with a 50% annual growth rate, production could reach 100 million units per year within a few years. He underscored the importance of robotics and AI for Tesla’s future, seeing them as part of the company’s strategy to lead not only in electric vehicles but also in AI and robotics – a vision that could make Tesla the most valuable company in the world.
Tesla, Inc. Q1 2025 financial results
On 22 April, Tesla released a weaker-than-expected Q1 2025 report. Its highlights are outlined below:
- Total revenue : 19.34 billion USD (–9%)
- Net income : 0.93 billion USD (–39%)
- Earnings per share : 0.27 USD (–40%)
- Operating margin : 2.1% (–343 basis points)
- Operating expenses : 2.75 billion USD (+9%)
- Capital expenditures : 1.49 billion USD (–46%)
Revenue by segment:
- Vehicle sales : 13.97 billion USD (–20%)
- Energy generation and storage : 2.73 billion USD (+67%)
- Services and other revenue : 2.63 billion USD (+15%)
Tesla’s Q1 2025 report reflected a challenging period for the company. Financial performance was lower than expected, with EPS (non-GAAP) at 0.27 USD, below the forecast of 0.42 USD. The automotive segment, the company’s primary revenue source, contracted by 20%, driven by a 13% decline in deliveries and lower average selling prices. These results highlight the impact of the temporary suspension of Model Y production, an aggressive pricing policy, and a reliance on regulatory credit revenues (595 million USD), without which the automotive division would have posted a loss. Macroeconomic factors, uncertainty surrounding trade policy, and reputational risks associated with Elon Musk’s public activity further complicated the company’s position.
Nevertheless, Tesla’s energy business showed an impressive 67% increase in revenue, reaching 2.73 billion USD and delivering a record gross profit, confirming the company’s success in the energy storage segment. Free cash flow turned positive, reaching 664 million USD compared with a deficit of 2.53 billion USD a year earlier, indicating effective capital management despite significant AI investments.
The strategic focus on autonomous technology remains the company’s key growth driver. The launch of Full Self-Driving (FSD) as a paid service was planned for June, with millions of autonomous vehicles projected to be deployed by the end of 2025.
The Optimus humanoid robot project, with a target production of one million units per year by 2029, underscored Tesla’s ambition to expand beyond the automotive sector.
The market reacted positively to the report, with the stock gaining over 7% following the release, reflecting confidence in these initiatives, particularly in light of Musk’s statements about prioritising Tesla. However, short-term risks remain considerable. The withdrawal of the growth forecast for deliveries in 2025 signalled demand uncertainty, exacerbated by potential tariffs and competition from Chinese manufacturers such as BYD. A 9% increase in operating expenses and the lack of clarity regarding the launch of more affordable models heightened this uncertainty.
Tesla’s management provided no specific forecasts for Q2 2025, stating instead that they would revise the 2025 outlook after the Q2 2025 results, citing ongoing uncertainty in the automotive and energy markets amid shifting trade policies and macroeconomic conditions. Analysts forecast Q2 2025 revenue of around 24.45 billion USD, although Tesla has not confirmed or revised this figure.
Given these factors, Tesla remains a highly risky investment. The energy segment, AI development, and long-term strategic vision offer the potential for substantial growth. However, delivering on these ambitions will require Elon Musk to return to active management of the company, as he promised. His involvement in US politics negatively affected Tesla’s reputation, and the company now faces the challenge of restoring trust among both consumers and investors.
Tesla, Inc. Q2 2025 financial results
Tesla released its Q2 2025 earnings report on 23 July. The key figures compared with the same period in 2024 are as follows:
- Total revenue : 22.49 billion USD (–12%)
- Net income : 1.39 billion USD (–23%)
- Earnings per share : 0.40 USD (–23%)
- Operating margin : 4.1% (–220 basis points)
- Operating expenses : 2.95 billion USD (–1%)
- Capital expenditures : 2.39 billion USD (+5%)
Revenue by segment:
- Automotive sales : 16.66 billion USD (–6%)
- Energy generation and storage : 2.78 billion USD (–7%)
- Services and other revenue : 3.04 billion USD (+17%)
Tesla’s Q2 2025 results were disappointing, with revenue down 12% year-on-year to 22.5 billion USD, and net income falling to 1.39 billion USD – the company’s weakest quarterly performance in a decade. The primary factor behind the decline was a 17% decrease in automotive sales revenue, totalling 16.66 billion USD. Operating profit dropped by 42%, while free cash flow totalled just 146 million USD. Overall liquidity also declined, reaching 36.8 billion USD at the end of the quarter. Tesla delivered 384,122 vehicles during the period, representing a 14% year-on-year decrease.
Overall, Q2 revealed serious challenges for Tesla, including a decline in global demand for electric vehicles, intensified competition (particularly from Chinese manufacturers), aggressive pricing, and the withdrawal of subsidies in the US. Taken together, these factors put pressure on margins and profitability. Notably, around 37% of Tesla’s quarterly profit came from the sale of regulatory credits (439 million USD). If these are fully phased out under new US policies, Tesla’s profit margin will come under further pressure. Additional negative factors included trade barriers and Elon Musk’s political activity, which drew criticism and weakened demand in Europe.
Despite this, Tesla still has several growth drivers. One of them is the planned launch of a fully autonomous robotaxi, which could create a new subscription-based model and scalable robotaxi fleet. Another is the affordable electric vehicle priced at approximately 25,000 USD, which could significantly expand the customer base. The development of energy storage and robotics platforms also promises growth over the next two years.
For Q3 2025, Tesla did not provide formal guidance for key indicators. Elon Musk warned that the upcoming quarters could be challenging, citing macroeconomic headwinds, the expiry of US incentives, new tariffs on Chinese-made components, and regulatory uncertainty in autonomous driving. The CFO added that production of the latest affordable model was expected to begin gradually. Wall Street analysts forecast Q3 revenue at around 22.2 billion USD, with EPS potentially declining to 0.39 USD, 25% below last year’s result.
Investor response to the quarterly report was negative – Tesla shares fell by more than 8% following the release. Analyst sentiment was mixed: some experts maintained a Buy recommendation with a price target of 500 USD, while others took a more conservative stance, recommending Sell with a target around 115 USD. A few of the most pessimistic analysts even forecast a collapse of the company, citing a target of 19 USD per share. Based on the P/E ratio, Tesla remains significantly overvalued compared with the sector average, making predictions of a decline in TSLA’s share price appear justified. However, it should be noted that a high P/E can also reflect expectations of strong growth – in Tesla’s case, this may be warranted by its technological leadership and scalable developments in autonomous driving, AI, and energy.
Tesla is currently undergoing a strategic transition. Profitability and revenue may continue to fluctuate in the coming quarters, but if the company successfully executes its roadmap, it could restore growth momentum. Investing in Tesla at this stage is a long-term wager on its capabilities in autonomy, artificial intelligence, and energy. Those less comfortable with high risk may prefer to wait until performance stabilises and new product demand is confirmed.
Tesla, Inc. Q3 2025 financial results
On 22 October, Tesla released its Q3 2025 report. The key figures compared with the same period in 2024 are as follows:
- Total revenue : 28.10 billion USD (+12%)
- Net profit : 1.77 billion USD (–29%)
- Earnings per share : 0.50 USD (–31%)
- Operating margin : 5.8% (–501 basis points)
- Operating expenses : 3.43 billion USD (+50%)
- Capital expenditure : 2.25 billion USD (–36%)
Revenue by segment:
- Automotive sales : 21.21 billion USD (+6%)
- Energy generation and storage : 3.42 billion USD (+44%)
- Services and other income : 3.48 billion USD (+25%)
In Q3 2025, Tesla delivered a record 497,099 electric vehicles (+7% y/y), supported by a surge in US demand ahead of the expiry of the 7,500 USD tax credit. The energy business also reached a record high, with 12.5 GWh of installed energy storage systems.
Revenue rose to a record level, but profit declined due to higher costs and changes in the revenue mix. The margin contracted as vehicle production costs increased, income from regulatory credit sales decreased, and, unlike last year, there was no one-off gain from FSD. Meanwhile, research and administrative expenses increased, resulting in a 40% year-on-year decline in operating profit. A key positive in the quarter was the record free cash flow of 3.99 billion USD and an increase in cash reserves to 41.6 billion USD.
The automotive segment increased revenue but saw lower profitability – rising component prices and tariffs offset the benefit of higher volumes. The energy business became the main growth driver, with Megapack and Powerwall contributing more revenue and profit. The services segment (including maintenance, charging stations, etc.) continued to grow at a double-digit rate.
The outlook remains uncertain. The company did not provide specific figures, citing risks related to tariffs, trade policy, and changes in government support. Tesla is betting that over time, a greater share of profit will come from software, artificial intelligence, and services. The company has sufficient financial reserves to support its plans, including the launch of robotaxis in California and the expansion of its energy business.
Overall, the quarter was mixed: strong volumes and cash flow offset weak profitability and rising costs. The main risks are a potential decline in US demand after the expiry of the tax credit and intensifying competition in China and Europe. Future stock valuations will depend on whether Tesla can stabilise automotive margins and turn growth in its energy and services businesses into sustainable profits.
Fundamental analysis of Tesla, Inc.
Below is the fundamental analysis of TSLA based on the results for Q3 2025:
- Liquidity and debt : Tesla maintains a robust financial cushion. Cash and short-term investments total 41.65 billion USD, up 4.9 billion USD from the previous quarter. Current assets are roughly twice the level of short-term liabilities, reflecting a solid liquidity buffer. Total debt stands at about 7.7 billion USD, almost all of which is non-recourse, meaning it is secured by assets and poses minimal risk to the company. As a result, Tesla’s net cash position is approximately 34 billion USD. The company earns more from its cash holdings than it pays in interest, with interest income totalling 439 million USD, compared with just 76 million USD in expenses.
- Cash flows : operating cash flow increased to 6.24 billion USD, supported by working-capital improvements and higher depreciation. Capital expenditure fell to 2.25 billion USD (–36% y/y), as the company has largely completed the main phase of its factory construction and is now spending less. As a result, free cash flow reached a record 3.99 billion USD (+46% y/y). Cash and investments rose to 41.65 billion USD, a comfortable level that provides ample capacity for financing new projects.
- Profitability and earnings : revenue grew 12%, but net profit declined 29%, and operating margin fell to 5.8% due to higher R&D and production costs and lower regulatory credit income. In addition, last year’s one-off FSD gain was not repeated. The strongest contributors to profit were the energy segment (+44% y/y) and services (+25% y/y), while the automotive business grew by only 6% y/y.
- Balance sheet strength : Tesla’s shareholders’ equity stands at nearly 80 billion USD, with total liabilities around 53 billion USD. The company continues to expand its tangible assets while reducing inventories to 12.3 billion USD, improving capital turnover. Inventory days declined from 24 to 10, and vehicle deliveries reached a record 497,000 units. The energy division also recorded a new high of 12.5 GWh in installed capacity.
Conclusion – fundamental view on TSLA: Tesla’s financial position remains exceptionally strong: the company is virtually debt-free, holds substantial cash reserves, and has achieved record free cash flow. The main challenge lies in the declining margin, driven by rising costs and reduced one-off income. However, the high level of liquidity provides Tesla with time to stabilise automotive profitability and expand into new areas such as energy, software, and services. Over the next 6–12 months, growth potential will depend not on revenue but on the company’s ability to improve margins and strengthen the resilience of the business.
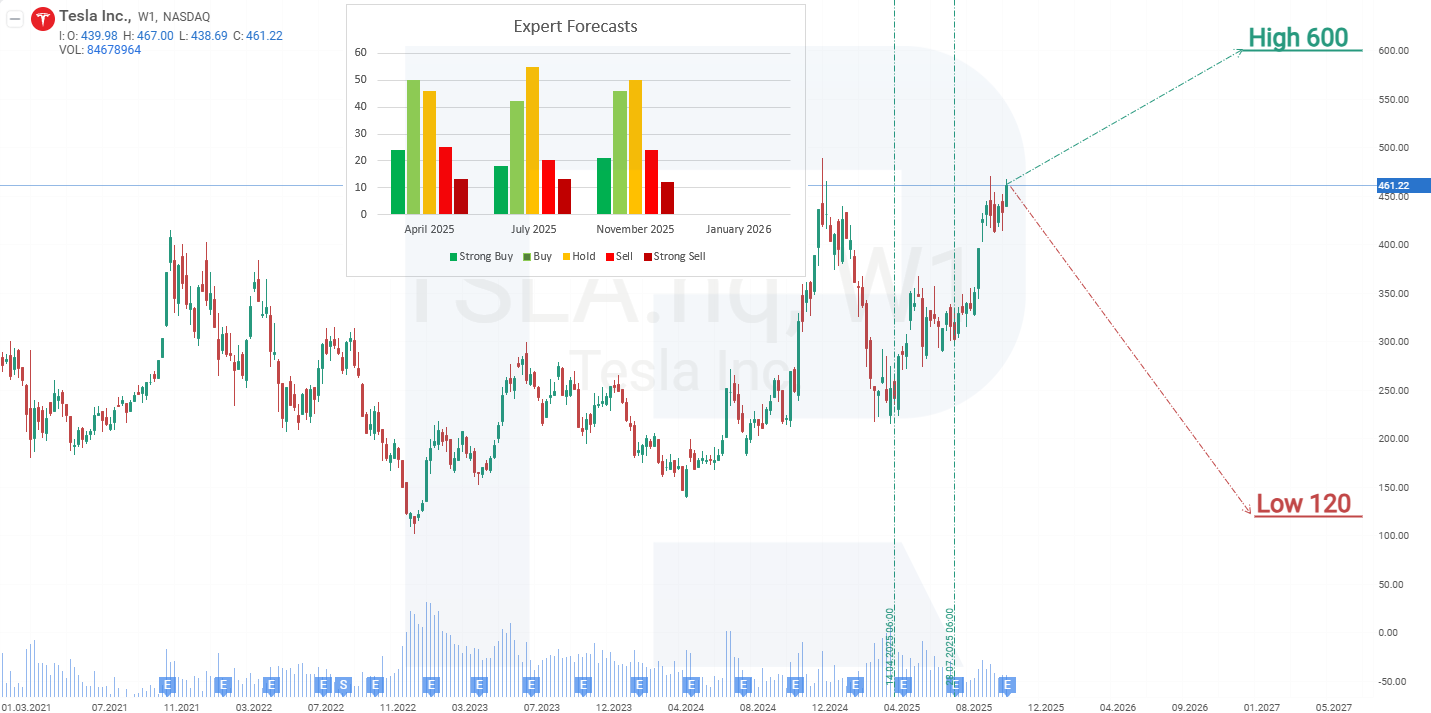
Expert forecasts for Tesla, Inc. shares for 2025
- Barchart : 14 of 42 analysts rated Tesla shares as a Strong Buy, 2 a Buy, 17 a Hold, and 9 a Strong Sell. The highest price target is 600 USD, and the lowest is 120 USD.
- MarketBeat : 21 out of 44 specialists rated the shares Buy, 12 Hold, and 11 Sell. The highest price target is 600 USD, and the lowest is 19 USD.
- TipRanks : 14 of 35 professionals recommended Buy, 11 Hold, and 10 Sell. The highest price target is 600 USD, and the lowest is 19 USD.
- Stock Analysis : 7 out of 31 experts rated the shares Strong Buy, 8 Buy, 10 Hold, 3 Sell, and 3 Strong Sell. The highest price target is 600 USD, and the lowest is 19 USD.
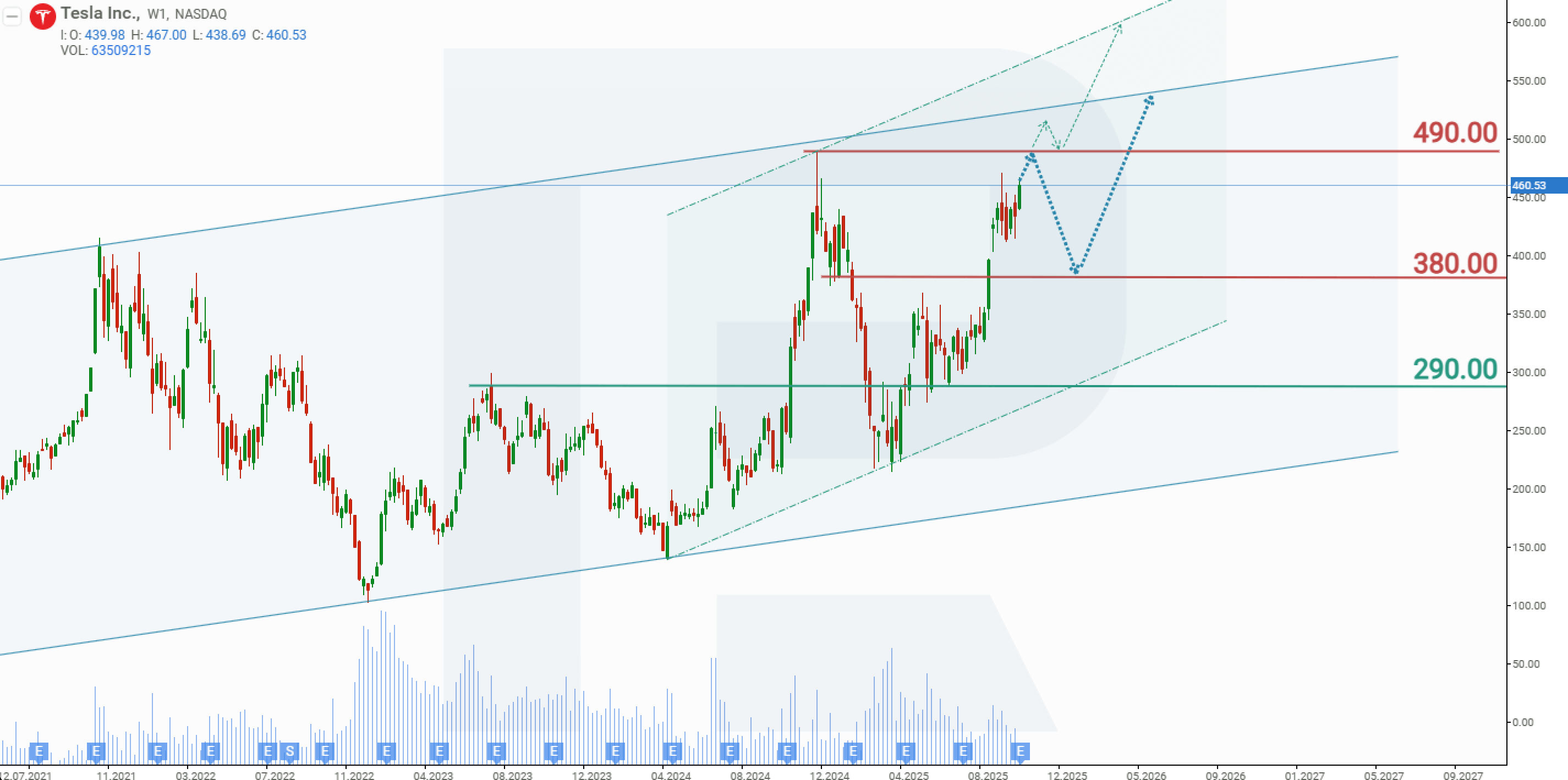
Tesla, Inc. stock price forecast for 2025
During the US presidential campaign, Elon Musk actively supported Donald Trump, and following Trump’s victory, Tesla’s share price began to rise. Between 4 November and 16 December, TSLA stock doubled in value, reaching an all-time high of 490 USD.
However, Musk’s subsequent involvement with DOGE had a negative impact on Tesla. Alongside intense competition and trade tensions, social media and progressive audiences increasingly called for a boycott of Tesla vehicles. As a result, TSLA shares fell by 56%, returning to levels last seen in early November 2024.
Musk’s return to active company management revived investor optimism. From April to November 2025, Tesla shares rose by 110%, gradually approaching their historical peak. Based on the current performance of Tesla’s share price, the following scenarios are considered for 2025:
The base-case forecast for Tesla shares suggests a test of resistance at 490 USD, followed by a pullback to 380 USD. This move would represent a correction preceding another upward wave. A rebound from the 380 USD support level would signal a potential resumption of growth toward the upper boundary of the channel near 550 USD.
The optimistic forecast for Tesla shares envisions a breakout above the all-time high of 490 USD, with TSLA continuing to climb toward the upper boundary of a faster ascending channel. In this case, the target level would be around 600 USD per share.
Tesla, Inc stock analysis and forecast for 2025Risks of investing in Tesla, Inc. shares
Considering the factors that could negatively impact the company’s future earnings is crucial when investing in Tesla, Inc. shares. Below are the main risks:
- Increased competition : Tesla faces growing competition from both traditional automakers, such as Volkswagen, General Motors, and Ford, as well as newer players, including BYD, Rivian, and Lucid. The competition is particularly fierce in China, where BYD has already surpassed Tesla in total electric vehicle production, including hybrid vehicles. Increased competition could lead to a loss of market share and price wars, reducing Tesla’s profitability.
- Economic conditions : elevated interest rates and economic downturns can impact consumer spending on expensive goods, such as electric vehicles. If interest rates remain high or increase further, the cost of financing a new Tesla could deter potential buyers.
- Policy changes : changes in government policy, such as the cancellation or reduction of tax incentives for electric vehicles, could affect demand for Tesla cars. State-level policies, such as a potential new credit system in California, where Tesla may not meet the criteria, could also further impact sales.
- Manufacturing and supply chain issues : delays or inefficiencies in ramping up production of new models could prevent Tesla from meeting market demand. Supply chain disruptions, chip shortages, or factory shutdowns could also affect production capabilities.
- Technological challenges : if Tesla’s advancements in autonomous driving or battery technology fail to meet expectations, or if competitors outpace Tesla in these areas, it could result in a loss of competitive advantage and investor confidence.
- Global Market Dynamics : fluctuations in exchange rates, trade tensions (especially with China, where Tesla has significant sales and production), or new tariffs could impact Tesla’s international revenues.
These factors, in combination, could influence Tesla’s revenue trajectory in 2025, creating a challenging environment where the company will need to navigate both internal and external challenges to maintain or improve its market position.
Forecasts presented in this section only reflect the author’s private opinion and should not be considered as guidance for trading. RoboForex bears no responsibility for trading results based on trading recommendations described in these analytical reviews.