AMD shares in 2026: continuation of growth or decline towards 150 USD?
AMD’s Q4 2025 report confirmed strong growth and robust momentum in the Data Center segment. However, the more cautious guidance for early 2026 disappointed investors. The market has begun to question whether the company can sustain its current growth trajectory, particularly amid intensifying competition from NVIDIA and its reliance on sales to China.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMD) delivered record financial results for Q4 2025 and exceeded market expectations. Revenue reached 10.3 billion USD, up 34% year-on-year. Non-GAAP net income rose to 2.5 billion USD, while earnings per share came in at 1.53 USD – significantly surpassing analysts’ forecasts. The Data Center segment expanded by 39% and accounted for more than half of the company’s total revenue. Revenue from the Gaming and Client segments also increased by 37%, reaching 3.9 billion USD.
Despite these strong reported figures, AMD shares fell by 17% following the earnings release. The decline was driven by guidance for Q1 2026: the company expects revenue of approximately 9.8 billion USD (±300 million USD), implying 32% year-on-year growth but a sequential decline of around 5% compared with the previous quarter. Investors had anticipated a more aggressive outlook, particularly given robust demand for AI-related solutions.
AMD cited seasonal weakness in the PC and gaming console segments, which the market interpreted as a sign that the company’s AI growth trajectory may still lag behind that of its main competitor, NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA). In addition, a significant share of Data Center growth came from China, which investors viewed as a source of uncertainty rather than evidence of a broad-based global trend.
This article examines AMD’s business model, the structure of its revenue streams, and its product offering in the AI market. It provides a fundamental analysis of AMD and a technical analysis of Advanced Micro Devices shares, forming the basis for the AMD stock forecast for 2026.
About Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is a US-based company founded in 1969 by Jerry Sanders and a group of fellow engineers. It designs and manufactures semiconductor devices, including processors, graphics chips, and server solutions. The company went public with an IPO on the NYSE in 1972 under the ticker AMD.
AMD is present in the rapidly expanding AI market with the following products:
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) for data centres: AMD produces Radeon Instinct microprocessors and has recently introduced new models in the MI series designed for high-performance computing and AI workloads. For example, the MI300 is a high-powered processor optimised for deep data analysis and large AI models.
- Radeon Open Compute (ROCm) software: AMD has developed an open-source software platform, ROCm, providing tools for AI development and high-performance computing on the company’s GPUs.
- Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs): following the acquisition of Xilinx, AMD expanded into FPGAs, which are widely used for AI applications, including signal processing and adaptive computing.
- Central Processing Units (CPUs): AMD also optimises its EPYC series processors to support AI computing in server solutions.
- Products for end devices: in addition to server solutions, AMD develops specialised GPUs and FPGAs for AI-powered end devices, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cameras, and medical equipment.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.’s main revenue streams
AMD’s revenue is generated from four key segments:
1. Data Center: includes EPYC server processors, AMD Instinct graphics accelerators for AI and scientific computing, and Xilinx FPGA solutions for specialised workloads in data centres.
2. Client segment: includes Ryzen and Athlon processors for desktop PCs and laptops, delivering high performance for general users and enthusiasts, and integrated graphics solutions for hybrid devices.
3. Gaming segment: includes Radeon GPUs for gaming PCs, integrated solutions for gaming laptops, and custom processors for gaming consoles such as PlayStation and Xbox.
4. Embedded segment: covers high-performance processors and graphics solutions for embedded systems in automotive electronics, industrial automation, medical devices, and telecommunications.
Advantages of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. in the semiconductor market
AMD has several strengths that enable it to compete effectively with key industry players, including Intel Corp. (NASDAQ: INTC) and NVIDIA Corp. (NASDAQ: NVDA). The company’s main advantages are outlined below:
- Processor architecture: AMD introduced the Zen architecture, which significantly enhanced performance and energy efficiency. The Ryzen (consumer) and EPYC (server) series have gained popularity thanks to their excellent performance-to-price ratio. In recent years, AMD has overtaken Intel in processor core and thread counts.
- Multi-core and multi-threaded solutions: AMD typically offers more cores and threads at the same price point, making its processors particularly attractive to users who require multitasking and high-performance computing (for example, for graphics, video editing, and data streaming).
- Innovations in graphics technology: although AMD still trails behind NVIDIA in certain high-performance GPU features, it holds a strong position thanks to its processors’ high data-processing throughput, offering a competitive price-to-performance ratio. With the RDNA and RDNA 2 series, AMD has made significant strides in improving the energy efficiency and performance of its graphics cards.
- EPYC server solutions: AMD’s EPYC line delivers an impressive performance-to-price ratio in the server segment, gaining traction among large corporations and data centres. These processors support more core counts per socket, reducing scaling costs for server infrastructure.
- CPU and GPU integration: AMD manufactures both processors and graphics chips, allowing it to develop integrated solutions for laptops and gaming consoles. For example, AMD supplies processors for PlayStation and Xbox consoles, which ensures a stable revenue stream and reinforces its market presence.
- Competitive pricing: AMD frequently offers lower-priced alternatives to Intel and NVIDIA, making its products attractive to a broader customer base, from enthusiasts to corporate clients.
- Rapid adoption of new technological processes: AMD collaborates with TSMC to swiftly implement advanced process nodes (such as 7 and 5 nm), enhancing energy efficiency and performance across its processors and graphics chips.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q3 2024 results
AMD released its Q3 2024 earnings report on 29 October, confirming continued revenue and net income growth. Below are the report’s key figures:
- Revenue: 6.82 billion USD (+18%)
- Net income: 0.77 billion USD (+158%)
- Earnings per share: 0.47 USD (+161%)
- Operating profit: 0.72 billion USD (+223%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Center: 3.55 billion USD (+122%)
- Client segment: 1.88 billion USD (+29%)
- Gaming segment: 462 million USD (–69%)
- Embedded segment: 927 million USD (–25%)
AMD benefited substantially from AI advancements, reflected in its Data Center segment, where revenue surged 122%, contributing to 52% of total revenue. The Gaming segment suffered the steepest decline (–69%), making it the weakest performer.
For Q4 2024, AMD projected revenue in the 7.20–7.80 billion USD range, with an average estimate of 7.50 billion. This implied a 22% year-on-year increase and a 10% rise compared to Q3 2024. However, the forecast fell slightly short of analysts’ expectations, sparking investor concerns, particularly amid intensifying competition in the AI market and a broader slowdown in segment growth.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q4 2024 results
AMD released its Q4 2024 earnings report on 4 February, showing a 37% decline in net income. The report highlights are outlined below:
- Revenue: 7.65 billion USD (+24%)
- Net income: 0.48 billion USD (–37%)
- Earnings per share: 0.29 USD (+29%)
- Operating profit: 0.87 billion USD (+155%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Center: 3.86 billion USD (+69%)
- Client segment: 2.31 billion USD (+58%)
- Gaming segment: 563 million USD (–59%)
- Embedded segment: 923 million USD (–13%)
2024 financial performance:
- Revenue: 25.78 billion USD (+14%)
- Net income: 1.64 billion USD (+92%)
- Earnings per share: 1.00 USD (+88%)
- Operating profit: 1.90 billion USD (+375%)
In Q4 2024, AMD CEO Lisa Su highlighted the company’s impressive performance, reporting a record annual revenue of 25.80 billion USD, up 14% from the previous year. This growth was mainly driven by a 94% surge in Data Center revenue and a 52% increase in the Client segment. Su also emphasised that AMD prioritises total revenue rather than the number of processors shipped, particularly amid concerns about potential CPU oversupply in the PC market.
The company attributed the decline in Q4 net income to a 17% rise in operating costs, primarily driven by higher research and development investments, especially in AI. Additionally, despite strong Data Center growth, AI GPU sales fell short of expectations, further impacting profitability.
For Q1 2025, AMD expects revenue of 7.10 billion USD, slightly exceeding analysts’ projections. However, Su warned about a potential slowdown in AMD Data Center sales, citing heightened competition, particularly from NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) in the AI processor market.
AMD management remains optimistic about 2025. Su projects strong double-digit growth in both revenue and EPS for the year. She also highlighted the long-term potential of AMD’s Data Center AI business, which generated over 5.00 billion USD in 2024 and is expected to eventually drive annual segment revenue into the tens of billions of dollars.
AMD management’s sentiment was cautiously optimistic, focusing on leveraging the company’s strengths in AI and computing to drive future growth while remaining agile in response to market shifts in weaker segments.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q1 2025 results
AMD released its Q1 2025 report on 6 May. Below are its highlights compared to the corresponding period in 2024:
- Revenue: 7.44 billion USD (+36%)
- Net income: 0.71 billion USD (+476%)
- Earnings per share: 0.44 USD (+529%)
- Operating profit: 0.81 billion USD (+2,139%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Center: 3.67 billion USD (+57%)
- Client segment: 2.29 billion USD (+68%)
- Gaming segment: 647 million USD (–30%)
- Embedded segment: 823 million USD (–3%)
AMD’s Q1 2025 financial performance strengthened confidence in the company as one of the leaders in the AI and data centre segment. AMD exceeded Wall Street expectations, reporting a 36% increase in revenue and a 476% rise in net income. Meanwhile, the key segments showed even stronger growth. The data centre segment increased sales by 57%, while PC processor revenue rose by 68%, driven by sustained demand for EPYC server processors, Instinct accelerators, and Ryzen chips for consumer PCs.
For Q2 2025, AMD management projected revenue to range between 7.1 and 7.7 billion USD but cautioned about potential losses of about 800 million USD, as the company might postpone or entirely abandon the sales of a significant amount of its AI chips in China. The reason is the new export restrictions imposed by the US government, which have banned exports of advanced technology to the Chinese market. As a result, these chips cannot be sold, and their cost will likely be written off as losses. However, AMD management warned about this as early as 16 April, so this information was most likely already factored into the current stock price. For 2025, CFO Jean Hu estimated revenue losses of 1.5 billion USD due to export restrictions.
Nevertheless, AMD management remained optimistic about 2025. The company anticipated double-digit growth in both revenue and EPS for the year, driven by its expanding AI portfolio and strategic partnerships. This signalled that AMD’s long-term potential remained promising despite external risks and short-term stock volatility.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q2 2025 results
AMD released its Q2 2025 earnings report on 5 August. Below are its highlights compared to the corresponding period in 2024:
- Revenue: 7.69 billion USD (+32%)
- Net income: 0.78 billion USD (–31%)
- Earnings per share: 0.48 USD (–30%)
- Operating profit: 0.90 billion USD (–29%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Center: 3.24 billion USD (+14%)
- Client segment: 2.49 billion USD (+67%)
- Gaming segment: 1.12 billion USD (+73%)
- Embedded segment: 824 million USD (–4%)
AMD ended Q2 2025 with record revenue of 7.7 billion USD, up 32% year-over-year. However, profitability was under pressure due to a one-time write-down of approximately 800 million USD, related to inventory and obligations tied to MI308 shipments to China, impacted by US export restrictions. This resulted in a decline in GAAP gross margin to 40% and non-GAAP margin to 43%. According to the company, the margin would have been around 54% without the write-down. The result was supported by record sales of EPYC server processors and Ryzen desktop processors, as well as a revival in the Gaming segment. However, the hit to margins and GAAP operating loss reminded the market of regulatory risks surrounding AI accelerators.
AMD’s segments delivered the following results: the Data Center segment generated approximately 3.2 billion USD in revenue, up 14% y/y, driven by EPYC sales, partially offsetting the impact of restrictions on the MI308. The Client and Gaming segments together contributed around 3.6 billion USD, with the Client segment reaching 2.5 billion USD, fuelled by strong demand for Zen 5-based desktop processors and a more favourable product mix. The Gaming segment rose to 1.1 billion USD, boosted by higher shipments of semi-custom chips for consoles and steady demand for Radeon GPUs. The Embedded segment generated 824 million USD, down 4% year-on-year, reflecting mixed demand across end markets. The company stated that it had achieved record free cash flow for the quarter, providing an additional cushion for AI investments.
The outlook for Q3 FY25 was confident. The company expected revenue of 8.7 billion USD ± 300 million USD, representing around 28% year-over-year growth and approximately 13% sequential growth, with a projected non-GAAP gross margin of about 54%. AMD had not included MI308 shipments to China in its Q3 guidance, as the issue was still under review by the US government. It was later reported that a scheme had been agreed under which AMD would obtain export licences for the MI308 in exchange for remitting 15% of revenue from sales in China.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q3 2025 financial results
AMD published its Q3 2025 financial results on 4 November 2025. The key figures, compared with the same period in 2024, are as follows:
- Revenue: 9.25 billion USD (+36%)
- Net income (non-GAAP): 1.97 billion USD (+31%)
- Earnings per share: 1.20 USD (+30%)
- Operating profit: 2.24 billion USD (+31%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Centre: 4.34 billion USD (+22%)
- Client segment: 2.75 billion USD (+46%)
- Gaming segment: 1.30 billion USD (+181%)
- Embedded segment: 857 million USD (–8%)
AMD reported a strong Q3 2025, beating market expectations. Adjusted (non-GAAP) revenue reached 9.25 billion USD, up 36% year-on-year, while adjusted earnings per share rose by 30% to 1.20 USD. This was slightly above analyst forecasts, which had anticipated revenue of 8.7–8.8 billion USD and EPS of 1.17 USD.
The gross margin remained high at 54%, indicating stable profitability and a recovery following a weak Q2 2025. Operating profit totalled 2.2 billion USD, with a margin of 24% – slightly below last year’s figure due to increased spending on research and development and promotion of AI products. AMD’s balance sheet remains healthy, with 7.2 billion USD in cash and investments against 3.2 billion USD in debt, resulting in a net cash position, demonstrating that the company is not reliant on borrowing.
The main growth driver for the quarter was the Data Centre segment, where revenue rose to a record 4.3 billion USD (+22% y/y), supported by strong sales of EPYC server chips and Instinct MI350 accelerators. The Client and Gaming businesses together generated about 4 billion USD (+73% y/y): the Client segment grew to 2.8 billion USD following robust Ryzen sales, and Gaming rose to 1.3 billion USD, driven by GPUs and console solutions. The Embedded segment was the only weak spot, declining by 8% to 0.86 billion USD.
For Q4 2025, management forecasted revenue of around 9.6 billion USD, with a possible ±0.3 billion USD deviation, implying year-on-year growth of 25%. The gross margin was expected to be approximately 54.5%. The company anticipated further increases in the Data Centre and Client segments and a gradual recovery in Embedded. The forecast did not account for sales to China due to uncertainty surrounding export restrictions.
Additionally, AMD outlined a new strategic plan for the next three to five years. The company targeted average annual revenue growth of more than 35%, an operating margin above 35%, and earnings per share exceeding 20 USD. For Data Centres, AMD targeted annual growth of over 60%, while other segments were expected to grow by more than 10%. Effectively, AMD indicated that in 2026 its focus would remain on AI accelerators and server processors, which are set to become the company’s primary sources of future growth.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Q4 2025 financial results
AMD released its Q4 2025 results on 3 February. Below are the key figures compared with the same period in 2024:
- Revenue: 10.27 billion USD (+34%)
- Net income (non-GAAP): 2.52 billion USD (+42%)
- Earnings per share: 1.53 USD (+40%)
- Operating profit: 2.85 billion USD (+41%)
Revenue by segment:
- Data Center: 5.38 billion USD (+39%)
- Client segment: 3.10 billion USD (+34%)
- Gaming segment: 0.84 billion USD (+50%)
- Embedded segment: 950 million USD (+34%)
AMD’s report appeared strong on an absolute basis, yet the market reaction was negative. The company posted revenue of 10.27 billion USD (+34% year-on-year), exceeding analysts’ expectations of 9.65–9.7 billion USD. Non-GAAP earnings per share came in at 1.53 USD versus the expected 1.32 USD. Overall, 2025 became a record year for AMD in terms of both revenue and profit, driven primarily by robust growth in the Data Center segment and stable demand for EPYC server processors and consumer Ryzen chips.
Guidance for Q1 2026 also came in above expectations. The company forecasts revenue of 9.8 billion USD (±300 million USD), compared with market expectations of around 9.4 billion USD. This suggests that AMD continues to see strong demand in AI and server-related solutions. Management emphasised its expectation of further expansion in the AI Data Center business, including EPYC processors and Instinct accelerators, and plans to broaden shipments to major enterprise and cloud customers in 2026.
Despite the solid headline figures, the share price declined as investors questioned the sustainability of part of the revenue base. Q4 revenue included one-off factors: 390 million USD from MI308 chip sales to China and 360 million USD from the release of inventory reserves. However, in Q1 2026, sales to China are expected to amount to only around 100 million USD due to US export restrictions. This implies that a portion of the growth recorded in the previous quarter will not be repeated, and the market interpreted this dynamic as a risk of revenue deceleration in the coming quarters.
Valuation multiples analysis for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Below are the key multiples for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc., based on the Q4 2025 results of the financial year, calculated at a share price of USD 214.
| Multiple | What it indicates | Value | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|
| P/E (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of earnings over the past 12 months | 80.7 | ⬤ Extremely expensive. The market is pricing in multiple years of earnings growth. |
| P/S (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of annual revenue | 10 | ⬤ High. For the semiconductor sector, a range of 5–7 is considered normal. |
| EV/Sales (TTM) | Enterprise value to sales, accounting for debt | 9.8 | ⬤ The valuation remains elevated. Investors are expecting AMD to replicate NVIDIA’s success. |
| P/FCF (TTM) | Price paid for 1 USD of free cash flow | 51.7 | ⬤ High valuation. The company needs to generate twice the cash to justify its current market cap. |
| FCF Yield (TTM) | Free cash flow yield to shareholders | 1.6% | ⬤ Low yield. Yield is below inflation and well below bond yields. Investors here are not looking for current cash flow, but betting on future growth. |
| EV/EBITDA (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit before depreciation and amortisation | 40 | ⬤ Normal. Typically, this would be a red flag, but for AMD, it’s considered normal. |
| EV/EBIT (TTM) | Enterprise value to operating profit | 91 | ⬤ Very high price for operating profit. A slowdown in growth or operational metrics could impact the stock price. |
| P/B | Price to book value | 5.53 | ⬤ Moderate. For a technology company with significant intellectual property, this is a moderate ratio. |
| Forward P/E | Forward price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio | 31.0–32.7 | ⬤ Moderate. This makes AMD stock more attractive for buying on a pullback. |
| Net Debt/EBITDA | Debt burden relative to EBITDA | 0.8 | ⬤ Moderate leverage |
| Interest Coverage (TTM) | Ability to cover interest expenses with operating profit | 27 | ⬤ Excellent interest coverage |
Valuation multiples analysis for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. – conclusion
If Advanced Micro Devices is assessed as a conventional mature company based on its current metrics, the valuation appears expensive and even overheated. A P/E of around 80.7 is relatively elevated. However, when considering a Forward P/E of approximately 31.0, the picture changes. This implies the market expects a sharp increase in net profit. If such growth materialises, the current high valuation could compress naturally as earnings expand. For AI chip companies, paying 31 USD for 1 USD of expected future earnings is generally regarded as acceptable.
At the same time, on a revenue and free cash flow basis, the company remains expensive, suggesting that an almost ideal growth scenario is already priced in. Investors are assuming that AMD will successfully increase its market share, including through competition with NVIDIA, and that it will not face major supply or demand issues. This implies that the margin for error is minimal: if anything deviates from the plan, the market reaction could be swift.
In conclusion, AMD is currently a bet on future profit growth. If forecasts for new products, including the Instinct and EPYC series, are realised, the current valuation with a Forward P/E of 31 may be reasonable for long-term investors. However, based on current revenue and cash flow metrics, the company remains expensive. If actual profits in 2026 fall short of expectations, a significant price drop may occur, as the optimistic scenario is already priced in.
This is a high-quality business with a strong balance sheet, but buying now is essentially a bet on future growth in the AI sector.
Expert forecasts for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.’s stock
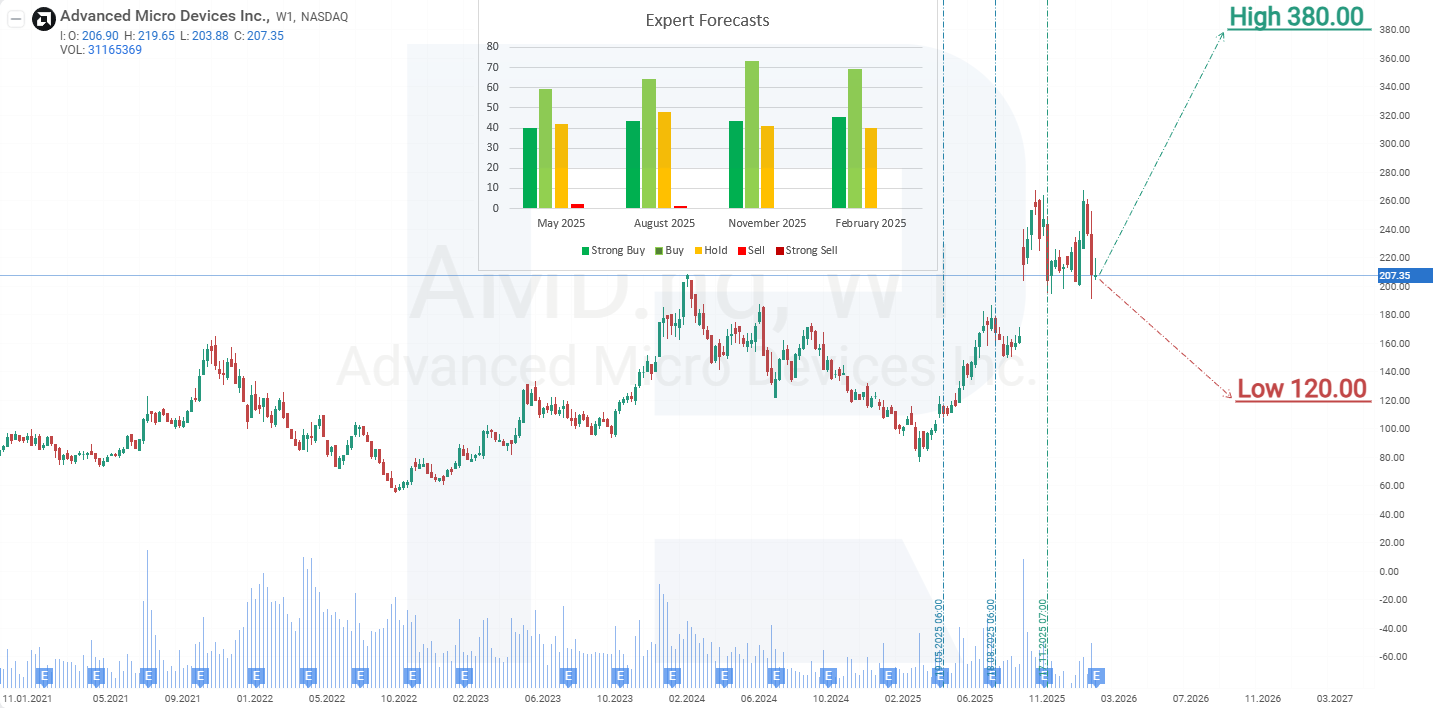
- Barchart: 31 out of 46 analysts rated the stock as a Strong Buy, 2 as a Moderate Buy, and 13 as Hold. The upper price target is 380 USD, with the lower bound at 140 USD.
- MarketBeat: 30 out of 40 specialists assigned a Buy rating to the stock, and 10 recommended Hold. The upper price target is 380 USD, with the lower bound at 210 USD.
- TipRanks: 24 out of 33 analysts recommended Buy, and 9 recommended Hold. The upper price target is 377 USD, with the lower bound at 210 USD.
- Stock Analysis: 14 out of 35 experts rated the stock as Strong Buy, 13 as Buy, and 8 as Hold. The upper price target is 345 USD, with the lower bound at 120 USD.
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. stock price forecast for 2025
On the weekly chart, Advanced Micro Devices shares traded within an ascending channel until October 2025. On 6 October 2025, a major agreement between AMD and OpenAI to supply AI chips, along with an option for OpenAI to acquire up to 10% of AMD’s shares, triggered a sharp rise in AMD’s stock price, causing the upper boundary of the ascending channel to break. However, the stock price growth then stalled, forming a double top on the chart, which signals a potential price decline. Based on the current price dynamics of AMD shares, the possible scenarios for 2026 are as follows:
The base-case forecast for Advanced Micro Devices shares suggests a break below the 194 USD support level, followed by a decline to 150 USD. At this level, a correction is expected to end, and a recovery in AMD’s stock price within the broader uptrend should resume. The growth target would be the resistance level at 340 USD. Investor caution is evident amid mixed results from the past quarter, in which sales to China accounted for a significant portion of revenue. Additionally, the overall market sentiment was negatively affected by Amazon’s EPS miss, as profits fell short of expectations. Investor interest may return if the stock price declines, and the company confirms sustained demand for AI solutions and its ability to convert this demand into profit and cash flow.
The optimistic forecast for Advanced Micro Devices stock suggests growth from the current level (214 USD). In this case, AMD shares could rise by the magnitude of the channel, reaching the resistance level around 340 USD.
Analysis and forecast for Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. stock for 2026Risks of investing in Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. stock
When investing in AMD shares, it is essential to consider the following risks:
- Intense competition: AMD faces tough competition from Intel Corp. (NASDAQ: INTC) and NVIDIA, which may lower prices or accelerate the introduction of new technologies, potentially impacting AMD’s market share negatively.
- Reliance on TSMC: AMD relies on TSMC to manufacture its chips. Any supply disruptions or delays in the introduction of new technology processes at TSMC (NYSE: TSM) could affect AMD’s market position.
- Demand fluctuations: the PC and server market is cyclical and depends on macroeconomic conditions. A decrease in device demand may reduce AMD’s revenue.
- Development of proprietary AI chips by consumers: large tech companies like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are investing in the development of their semiconductors for data centres and specialised tasks. This reduces their reliance on external suppliers, including AMD. If these corporations continue to increase spending on developing their proprietary chips, it could limit AMD’s overall market, reduce its share in the data centre segment, and slow its revenue growth over the long term.
Forecasts presented in this section only reflect the author’s private opinion and should not be considered as guidance for trading. RoboForex bears no responsibility for trading results based on trading recommendations described in these analytical reviews.